The core component
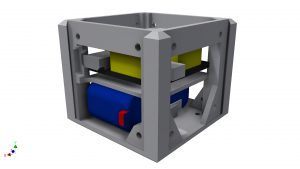
This is the core component of which each robot should have exactly one. This cube holds the Arduino board as well as the battery that powers the robot. Furthermore it holds an IMU which has accelerometers and gyros on 3 axes. When fabricating your robot try to place/orient the core at a well accessible location of the robot, as you will quite often have to connect the battery to the charger, the Arduino to your computer, or adjust the connections on the Arduino.
| IO id |
Input/output device |
| 0 |
x-accelerometer |
| 1 |
y-accelerometer |
| 2 |
z-accelerometer |
| 3 |
x-gyroscope (angular velocity) |
| 4 |
y-gyroscope (angular velocity) |
| 5 |
z-gyroscope (angular velocity) |
|
|
Structural components
Fixed brick
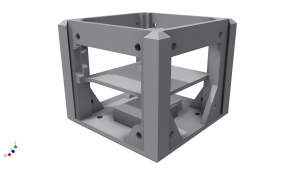
| This is the main structural component of the robot. It resembles the core component but does not bear the electronics of the latter. The side length of the cube is 4.65cm. Each side can be connected to another component. |
|
Parametric bar joint
| The parametric bar joint allows the introduction of fix angles into your robot and can also be useful depending on the needs to space components of your robot. Three parameters can be controlled: The length of the joint (H, between 2 and 10 centimeters), its tilt (alpha, between -90 and 90 degrees) and its rotation (beta, however this is currently restrictedto be 0 degrees). Compared to the fixed brick or core component, the parametric bar joint is somewhat frail and should not be exposed to too much mechanical stress. |
|
Moving joints
For all active moving joints, the signal from the neural network corresponds to servo position, not velocity.
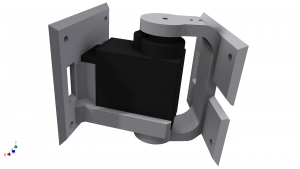
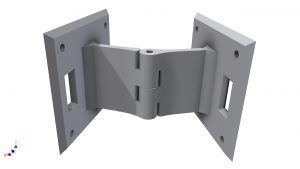
Active or passive hinge joint
| IO id |
Input/output device |
| 0 |
Motor of active hinge |
|
|
|